Nigeria Faces Economic Turmoil Amid Fuel Subsidy Cuts and Currency Devaluation
Nigeria faces economic turmoil from fuel subsidy cuts and currency devaluation, yet the tech sector, especially fintech, thrives amid challenges.
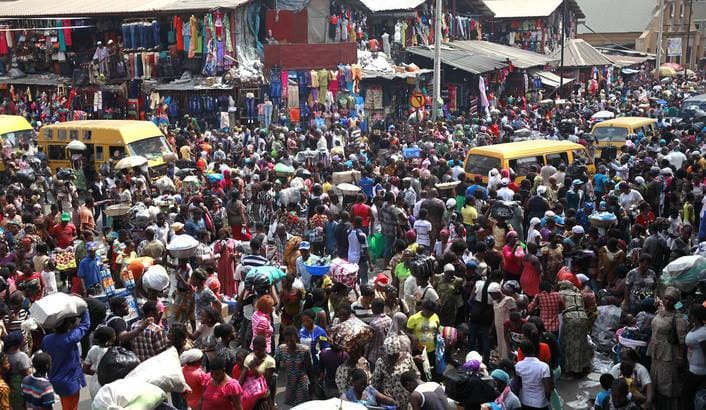

In Nigeria, long lines snake around banks and ATMs as citizens wait hours just to withdraw enough money for daily needs. Tensions have erupted into violence, with frustrated individuals attacking bank employees and demonstrators setting buildings ablaze. This turmoil stems from drastic economic policies implemented by President Bola Tinubu since his inauguration in May 2023. The removal of fuel subsidies, in place since the 1970s, and the abandonment of a long-standing currency peg have caused the naira to plummet and inflation to soar above 35%.
Economic Impact on Daily Life
With inflation eroding salaries, many employees have stopped going to work, unable to afford even their bus fares. Companies have adjusted by selling products in smaller sachets, catering to consumers who can no longer afford larger packages. Over 75% of Nigerian households now live on just $3-5 per day, amplifying the economic strain.

Nigeria: A Nation of Contrasts
Nigeria, a nation of contrasts and immense potential, is home to over 250 ethnic groups and 500 languages. Once Africa's largest economy, it has now slipped to fourth place. Despite the economic hardships, Nigeria remains a vibrant cultural hub, boasting the world’s second-largest film industry, Nollywood, which produces about 2,500 films annually. Nigerian musicians like Rema, Burna Boy, and Wizkid continue to draw international crowds.
Historical Context: From Agriculture to Oil Dependency
The country's economic journey began in the early 20th century as a key agricultural exporter under British colonial rule, with products like cocoa, palm oil, and groundnuts. However, the discovery of oil in the 1950s shifted Nigeria’s focus to oil dependency. The 1970s oil boom brought immense wealth but also laid the groundwork for corruption and economic instability. Fluctuations in global oil prices in the 1980s and 1990s exposed the economy's vulnerability, leading to severe recessions and increased debt.
The Curse of Oil Wealth
Corruption, fueled by oil revenues, has plagued Nigeria's political and economic systems. The Corruption Perception Index ranks Nigeria near the bottom globally. Mismanagement of oil wealth has hindered investment in critical sectors like health, education, and infrastructure. Public institutions suffer from inefficiency, and foreign direct investment has been declining since 2012, exacerbating poverty levels.
Tech Sector: A Beacon of Hope
Despite these challenges, Nigeria’s tech sector, particularly fintech, is booming. Driven by a young, tech-savvy population and high mobile phone usage, fintech companies like FairMoney, PiggyVest, and Bamboo are thriving. The number of tech start-ups in Nigeria tripled from 2017 to 2023, reaching around 217 companies. However, the sector faces hurdles such as unreliable power and internet, and an unpredictable regulatory environment.
Looking Ahead: Innovation and Diversification
Nigeria’s future depends on innovation and diversification. The burgeoning tech sector, dubbed 'Silicon Lagoon,' attracts global interest, with startups in fintech, agritech, and e-commerce leading the charge. Investments in renewable energy aim to reduce reliance on oil and address energy shortages. Young entrepreneurs are harnessing technology to solve local problems, offering hope for a more balanced and sustainable future.
Solution to Nigeria’s problem is this ,
— rharl🇳🇬🇦🇺🇨🇦🍁 (@rharlpon) July 31, 2024
The Govt has to stop running fiscal surpluses; especially in a growing economy like ours.
Cut senate, presidential expenses & more, settle pending debts with the funds without incurring more loans.
Simple, Is it difficult?
BREAKING NEWS pic.twitter.com/HP1A4qotn3
A Promising Future Despite Challenges
Nigeria's rich resources, energetic population, and emerging sectors provide a foundation for potential growth. Despite current economic challenges, the spirit of innovation and determination among Nigerians remains strong, promising a brighter future.